Help

The Basics:
Preferred file types from PC & Mac:
- Microsoft Word
- Microsoft Excel
- Microsoft Publisher
- Microsoft PowerPoint
- Adobe InDesign CS5 or later (Packaged please... see tutorial)
- Adobe Illustrator CS5 or later
- Adobe Photoshop CS5 or later
- High Resolution PDF (We like this file the best!)
*Templates from Etsy, Canva, and other online services also accepted!
Setting Up a File:
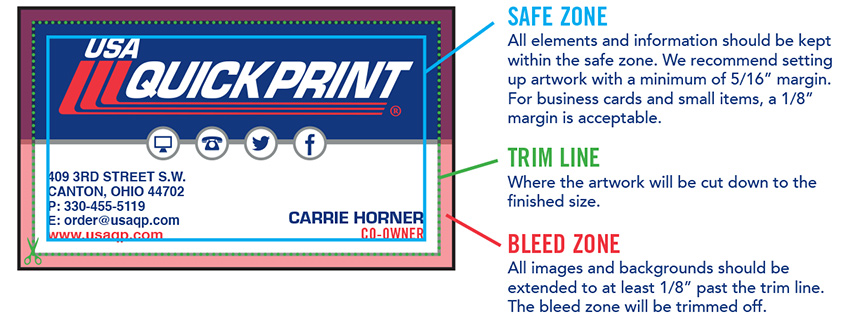

Fonts & Links:
Fonts used in files should be supplied in a separate folder marked "fonts". When sending an Illustrator or InDesign file, convert all type to outlines when possible.
If photos, logos, etc. are used, these should be supplied in a folder marked "links".
When working in Adobe InDesign, fonts and links can be automatically packaged. See Adobe InDesign’s tutorial or contact us for help.
Colors:
Please assign/specify spot colors, CMYK, grayscale, etc.

Questions? Call us at 330-455-5119 or send us an email via the contact form.
Revised: June 2018
Printing Glossary of Terms
The world of printing terminology can be very complex. So we've compiled a glossary with terms and definitions to help our customers understand the world of printing a little better. If you'd like further help with any of the topics discussed here, please feel free to contact us. Also, be sure to check out our artwork guidelines for some helpful tips on submitting your design.
About the List of Terms
The following list contains the most common terms, abbreviations and acronyms used around our printing shop. This is not a complete list and is obtained from Pocket Pal: The Handy Little Book of Graphic Arts Production, 19th Edition.
-
AA
Abbreviation for author’s alterations.
-
Absorption
In paper, the property which causes it to take up liquids or vapors in contact with it. In optics, the partial suppression of light through a transparent or translucent material.
-
Accordion
Fold In binding, a term used for two or more parallel folds which open like an accordion.
-
Additive Primaries
In color reproduction, red, green and blue (RGB). When lights of these colors are added together, they produce the sensation of white light.
-
Adobe Acrobat
Software that embodies the PDF format.
-
Against the Grain
Folding or feeding paper at right angles to the grain direction of the paper. Also called crossgrain.
-
Airbrush
In artwork, a small pressure gun shaped like a pencil that sprays watercolor pigment. Used to correct and obtain tone or graduated tone effects. In platemaking, used with an abrasive-like pumice to remove spots or other unwanted areas. In electronic imaging, a retouching technique.
-
Alkaline Paper
Paper made with a synthetic alkaline size and an alkaline filler like calcium carbonate which gives the paper over four times the life (200 years) of acid-sized papers (40-50 years).
-
AM (Amplitude Modulation)
Halftone screening, as opposed to FM screening, has dots of variable size with equal spacing between dot centers. See halftone.
-
Analog Color Proof
Off-press color proof made from separation films.
-
Anti-offset or Set-off Spray
In printing, dry spray of finely powdered starch used on press to prevent wet ink from transferring from the top of one sheet to the bottom of the next sheet. This also separates the sheets on a micro level so oxygen can react with the ink to enhance ink drying.
-
Antique Finish
A term describing the surface, usually on book and cover papers, that has a natural rough finish.
-
Aperture
In photography lens opening or lens stop expressed as an f/no, such as f/22.
-
Apochromatic
In photography color-corrected lenses which focus the three colors, blue, green and red, in the same plane.
-
APR (Automatic Picture Replacement)
The replacement of a low resolution image by a high resolution image.
-
Argon Laser
A very strong blue laser that peaks at 470 nanometers.
-
Art
All illustration copy used in preparing a job for printing.
-
Ascender
That part of a lowercase letter which rises above the main body, as in “b.”
-
ASCII (American Standard Code for Information Interchange)
A standard means of representing text as numerical data.
-
Automatic Processor
In photography a machine to automatically develop, fix, wash and dry exposed photographic film. In platemaking, a machine to develop, rinse, gum and dry printing plates.
-
Backbone
The back of a bound book connecting the two covers; also called spine.
-
Backing Up
Printing the reverse side of a sheet already printed on one side.
-
Bad Break
In composition, starting a page or ending a paragraph with a single word, or widow.
-
Basic Size
Basic size: In inches, 8.5 x 11 for letterhead, 8.5 x 14 for legal, 11 x 17 for ledger.
-
Basis Weight
The weight in pounds of a ream (500 sheets) of paper cut to a given standard size for that grade; e.g., 500 sheets 25 x 38” of 50-lb. book paper weigh 50 pounds.
-
Beta Site
A test site for computer software or systems.
-
Bezier Curve
The description of a character, symbol or graphic by its outline used by drawing programs to define shapes.
-
Bimetal Plate
In lithography a plate used for long runs in which the printing image base is usually copper and the non-printing area is aluminum, stainless steel or chromium.
-
Bit
In computers, the basic unit of digital information; contraction of Binary digit.
-
Bit-depth
1.The number of bits of tonal range capability of the pixels in an image. For example, RGB 24-bit color means a pixel depth of 8 bits per color, or 256 levels per color. 2. The number of bits of tonal range capability of the spots of an output device.
-
Bitmap
In computer imaging, the electronic representation of a page, indicating the position of every possible spot (zero or one).
-
Black-and-White
Originals or reproductions in single color, as distinguished from multicolor. Abbreviation: B&W or B/W.
-
Blanket
In offset printing, a rubber-surfaced fabric which is clamped around a cylinder, to which the image is transferred from the plate, and from which it is transferred to the paper.
-
Bleed
An extra amount of printed image which extends beyond the trim edge of the sheet or page.
-
Blind Embossing
A design which is stamped without metallic leaf or ink, giving a bas-relief effect.
-
Blind Image
In lithography an image that has lost its ink receptivity and fails to print.
-
Blowup
An image enlargement.
-
Body
In inkmaking, a term referring to the viscosity, or consistency, of an ink (e.g., an ink with too much body is stiff).
-
Body Type
A type used for the main part or text of a printed piece, as distinguished from the heading.
-
Bold-face Type
A name given to type that is heavier than the text type with which it is used.
-
Bond Paper
A grade of writing or printing paper where strength, durability and permanence are essential requirements; used for letterheads, business forms, etc.
-
Book Paper
A general term for coated and uncoated papers.
-
BPI
Bits per inch.
-
BPS
Bits per second.
-
Break for Color
In artwork and composition, to separate the parts to be printed in different colors.
-
Brightness
In photography light reflected by the copy. In paper, the reflectance or brilliance of the paper.
-
Brochure
A pamphlet bound in booklet form.
-
Bulk
The degree of thickness of paper. In book printing, the number of pages per inch for a given basis weight. Or sometimes referred to as high qty of product ordered.
-
Bump Exposure
In photography an exposure in halftone photography, especially with contact screens, in which the screen is removed for a short time. It increases highlight contrast and drops out the dots in the whites.
-
Burn
In platemaking, a common term used for a plate exposure.
-
Byte
In computers, a unit of digital information, equivalent to one character or 8 to 32 bits, 64 bits, etc.
-
CADD (Computer-Aided Drafting or Design)
In graphics, the production of drawings and plans for architecture and engineering systems. CADD systems are specialized workstations or high-performance personal computers that employ CADD software packages and input devices such as graphic tablets and scanners.
-
Calendar Rolls
A set or stack of horizontal cast-steel rolls with polished ground surfaces at the end of a paper machine. The paper is passed between the rolls to increase the smoothness and gloss of its surface.
-
Caliper
The thickness of paper, usually expressed in thousandths of an inch (mils). In board, however, it is expressed as “points.”
-
Camera-Ready
Copy which is ready for photography.
-
Caps and Small Caps
Two sizes of capital letters made in one size of type, commonly used in most roman typefaces.
-
Case
In bookbinding, the covers of a hardbound book.
-
Cast Coated
Coated paper dried under pressure against a polished drum to produce a high-gloss enamel finish.
-
CCD (Charge Coupled Device)
In digital prepress, a semiconductor light sensitive electronic device that emits an electrical signal proportional to the amount of light striking it. Used in scanners and video cameras.
-
CD-ROM (Compact Disc Read Only Memory)
In digital prepress, a laser-encoded optical storage disk that can store 650 megabytes to over 1 gigabyte of data on a disk about the size of a traditional 51/4-inch floppy disk.
-
CEPS (Color Electronic Prepress System)
In digital prepress, a high-end computer-based system that is used to color correct scanner images and assemble image elements into final pages. They are device-dependent systems.
-
Chalking
In printing, a term which refers to improper drying of ink. Pigment dusts off because the vehicle has been absorbed too rapidly into the paper.
-
Character Generation
The production of typographic images using font master data. Generated to screens or output devices.
-
Chemical Pulp
In papermaking, treatment of ground wood chips with chemicals to remove impurities such as lignin, resins and gums. There are two types, sulfite and sulfate.
-
Chemistry
In photography and platemaking, a term used to describe the composition of processing solutions.
-
Chokes and Spreads
Overlap of overprinting images to avoid color or white fringes or borders around image detail. Called trapping in digital imaging systems.
-
Closed Loop System
In printing, a completely automatic control system.
-
CMY (Cyan, Magenta, Yellow)
Subtractive primary colors, each of which is a combination of two additive primary colors (RGB).
-
CMYK (Cyan, Magenta, Yellow, Black)
The subtractive process colors used in color printing. Black (K) is added to enhance color and contrast.
-
Coated Paper
Paper having a surface coating which produces a smooth finish. Surfaces vary from eggshell to glossy.
-
Coating
In platemaking, the light-sensitive polymer or mixture applied to a metal plate. in printing, an emulsion, varnish or lacquer applied over a printed surface to protect it.
-
Collate
In binding, the gathering of sheets and signatures.
-
Color Balance
The correct combination of cyan, magenta and yellow to (1) reproduce a photograph without a color cast, (2) produce a neutral gray, or (3) reproduce the colors in the original scene or object.
-
Color Correction
Any method such as masking, dot-etching, re-etching and scanning, used to improve color.
-
Color Filter
A sheet of dyed glass, gelatin or plastic, or dyed gelatin cemented between glass plates, used in photography to absorb certain colors and transmit others. The filters used for color separation are red, green and blue. (ROB)
-
Color Management
It is broadly defined as a system of hardware, software and procedures that are calibrated to best insure color accuracy and repeatability throughout the production process. See ICC.
-
Color Proofs
See analog color proof, direct digital color proof.
-
Color Separation
In photography the process of separating color originals into the primary printing color components in negative or positive form using RGB filters.
-
Colorimeter
An instrument for measuring color the way the eye sees color.
-
Commercial Register
Color printing on which the misregister allowable is within ± one row of halftone dots.
-
Commingled Mailing
Combined mailing of magazines of the same size to the same address to save costs.
-
Common Impression Cylinder Press
In flexography, letterpress, lithography and digital printing, a press with a number of printing units around a large impression cylinder.
-
Computer-to-Plate
See CTP.
-
Computer, Analog
A computer that solves a mathematical problem by using analogs, like voltage or density, of the variables in the problem.
-
Computer, Digital
A computer that processes information in discrete digital form.
-
Computerized Composition
An all-inclusive term for the use of computers to automatically perform the functions of hyphenation, justification and page formatting.
-
Condensed Type
A narrow or slender typeface.
-
Condensed Type
A narrow or slender typeface.
-
Conductivity
A property of fountain solutions that must be controlled along with pH.
-
Contact Print
A photographic print made from a negative or positive in contact with sensitized paper, film or printing plate.
-
Contact Screen
A halftone screen on film having a dot structure of graded density, used in vacuum contact with the photographic film to produce halftones.
-
Continuous Tone
An image which contains gradient tones from black to white.
-
Contone
Abbreviation for continuous tone.
-
Contract Proof
A color proof representing an agreement between the printer and the customer regarding how the printed product will look.
-
Contrast
The tonal gradation between the highlights, middle tones and shadows in an original or reproduction.
-
Copy
Any furnished material (typewritten manuscript, pictures, artwork, etc.) to be used in the production of printing.
-
Copy Preparation
Directions for, and checking of, desired size and other details for illustrations, and the arrangement into proper position of various parts of the page to be photographed or electronically processed for reproduction.
-
Cover Paper
A term applied to a variety of papers used for the covers of catalogs, brochures, booklets and similar pieces.
-
Creep
Sometimes called “push out,” it is the distance margins shift when paper is folded and/or inserted during finishing. The amount of creep will vary depending on both the number and thickness of the sheets and must be compensated for during layout and imposition. See shingling.
-
Crop
To eliminate portions of the copy, usually on a photograph or plate, indicated on the original by cropmarks.
-
Cross Direction
In paper, the direction across the grain. Paper is weaker and more sensitive to changes in relative humidity in the cross direction than the grain direction.
-
Crossmarks
See register marks.
-
CTP (Computer-to-Plate)
In platemaking, Computer-to-Plate systems or platesetters eliminate the need for having a separate film to plate exposure system.
-
Curl
In paper, the distortion of a sheet due to differences in structure or coatings from one side to the other, or to absorption of moisture on an offset press.
-
Cutoff
In web printing, the cut or print length.
-
Cutscore
In diecutting, a sharp-edged knife, several thousandths of an inch lower than the cutting rules in a die, made to cut part way into the paper or board for folding purposes.
-
Cyan
Hue of a subtractive primary and a 4-color process ink. It reflects or transmits blue and green light and absorbs red light.
-
Cylinder Gap
In printing presses, the gap or space in the cylinders of a press where the mechanism for plate (or blanket), clamps and grippers (sheetfed) is housed.
-
DCS (Desktop Color Separation)
In digital prepress, a data file defined to assist in making color separations with desktop systems. Using DCS five files are created: four color files, containing the cyan, magenta, yellow and black image data, and a composite color preview of the color image.
-
Deckle
In papermaking, the width of the wet sheet as it comes off the wire of a paper machine.
-
Deckle Edge
The untrimmed feathery edges of paper formed where the pulp flows against the deckle frame.
-
Densitometer
In photography a photoelectric instrument which measures the density of photographic images, or of colors. In printing, a reflection densitometer is used to measure and control the density of color inks on the substrate.
-
Density
The degree of darkness (light absorption or opacity) of a photographic image.
-
Descender
That part of a lowercase letter which extends below the main body, as in “p.”
-
Desktop Publishing
Process of composing pages using a standard computer, off-the-shelf software, a device independent page description language like PostScript and outputting them on a printer or imagesetter.
-
Developer
In photography the chemical agent and process used to render photographic images visible after exposure to light. In lithographic platemaking, the material used to remove the unexposed coating.
-
Device Dependent
A characteristic of CEPS. See CEPS.
-
Device Independent
The characteristic of a computer program or system that allows different output devices to image the same file more or less the same.
-
Diazo
In photography a non-silver coating for contact printing. In offset platemaking, a light-sensitive coating used on presensitized and wipe-on plates.
-
Die-Stamping
An intaglio process for the production of letterheads, business cards, etc., printing from lettering or other designs engraved into copper or steel.
-
Diecutting
The process of using sharp steel rules to cut special shapes for labels, boxes and containers, from printed sheets. Diecutting can be done on either flatbed or rotary presses. Rotary diecutting is usually done inline with the printing.
-
Diffusion Transfer
In photography and platemaking, a system consisting of a photographic emulsion on which a negative is produced, and a receiver sheet on which a positive of the image is transferred during processing.
-
Digital Asset Management (DAM)
Also known as Media Asset Management, it is a segment of the content management market focused on the systematic cataloging and management of digital media (text, images, video and audio) and some physical media to enable their efficient storage, retrieval and reuse.
-
Digital Color Proof
A color proof produced from digital data without the need for separation films.
-
Digital Inks
See toners.
-
Digital Photography
Uses a CCD or CMOS sensor in place of film to capture images electronically. Digital photography is used widely by photojournalists and is being used increasingly by both professional photographers and consumers as well.
-
Digital Plates
Printing plates that can be exposed by lasers or other high energy sources driven by digital data in a platesetter.
-
Digital Printing
Printing by plateless imaging systems that are imaged by digital data from prepress systems.
-
Digitizer
A computer peripheral device that converts an analog signal (images or sound) into a digital signal.
-
Dimensional Stability
Ability to maintain size; resistance of paper or film to dimensional change with change in moisture content or relative humidity.
-
Direct Screen Halftone
In color separation, a halftone negative made by direct exposure from the original on an enlarger or by contact through a halftone screen.
-
Display Type
In composition, type set larger than the text.
-
Dithering
In computer graphics, a technique for alternating the values of adjacent dots or pixels to create the effect of intermediate values. Dithering refers to the technique of making diff9rent colors for adjacent dots or pixels to give the illusion of a third color.
-
Doctor Blade
In gravure, a knife-edge blade pressed against the engraved printing cylinder which wipes away the excess ink from the non-printing areas.
-
DOS (Disk Operating System)
In digital imaging, a program containing instructions for a computer to read and write data to and from a disk. An operating system (set of programs) that instructs a disk-based computing system to manage resources and operate peripheral equipment.
-
Dot
Smallest screening element. Common usage does not clearly differentiate between dots and spots. A dot is composed of many spots. The fineness of a halftone screen is measured in ‘lines per inch’ or Ipi. In AM screening the dots vary in size. In FM screening the dots are all the same size.
-
Dot Gain
In printing, a defect in which dots print larger than they should, causing darker tones or stronger colors.
-
Dots Per Inch (DPI)
A measure of the resolution of a screen image or printed page.
-
Download
Sending information to another computer or to an output.
-
Draw-Down
In inkmaking, a term used to describe ink chemist’s method of roughly determining color shade. A small glob of ink is placed on paper and drawn down with the edge of a putty knife or spatula to get a thin film of ink.
-
Drop-Out
Portions of originals that do not reproduce, especially colored lines or background areas (often on purpose).
-
Drum Scanner
Uses photo multiplier tubes (PMT) and produces color separations with higher resolution and dynamic range than CCD scanners.
-
Dryer
In inkmaking, a substance added to hasten drying. DTP Acronym for Desktop Publishing.
-
Dummy
A preliminary layout showing the position of illustrations and text as they are to appear in the final reproduction. A set of blank pages made up in advance to show the size, shape, form and general style of a piece of printing.
-
Duotone
In photomechanics, a term for a two-color halftone reproduction from a one-color photograph.
-
Duplex Paper
Paper with a different color or finish on each side.
-
Duplicating Film
A film for making positives from positives, and negatives from negatives.
In color reproduction, a special film used for making duplicates of color transparencies -
DVD (Digital Video or Versatile Disk)
A disk that can store audio, video and computer data at four or more gigabytes per disk. dynamic range Density difference between highlights and shadows of scanned subjects.
-
EDG (Electronic Dot Generation)
In digital imaging, a method of producing halftones electronically on scanners and prepress systems.
-
Electronic Printing
In digital printing, any technology that reproduces pages without the use of traditional ink, water or chemistry or plates. Also known as plateless printing.
-
Electrophotography
Image transfer systems used in copiers to produce images using electrostatic forces and toners.
-
Electrostatic Assist
In gravure, use of electrostatic forces to help draw ink from gravure cells to reduce skips in highlights.
-
Electrostatic Plates
Plates for high-speed laser printing using zinc oxide or organic photoconductors.
-
Electrotype
Duplicate relief plate used for letterpress printing.
-
Elliptical Dot
In halftone photography elongated dots which give improved gradation of tones particularly in middle tones and vignettes — also called chain dots.
-
Em
In composition, a unit of measurement exactly as wide and high as the point size being set. So named because the letter “M” in early fonts was usually cast on a square body.
-
Embossed finish
Paper with a raised or depressed surface resembling wood, cloth, leather or other pattern.
-
Embossing
Impressing an image in relief to achieve a raised surface; either overprinting or on blank paper (called blind embossing).
-
EME (Electromechanical Engraver)
In gravure, machine used to make gravure printing cylinders.
-
Emulsion Side
In photography the side of the film coated with the silver halide emulsion.
-
En
In composition, one-half the width of an em.
-
Enamel
A term applied to a coated paper or to a coating material on a paper.
-
English Finish
A grade of book paper with a smoother, more uniform surface than machine finish.
-
EPS (Encapsulated PostScript)
In digital prepress, a file format used to transfer graphic images within compatible applications. A file containing structured PostScript code, comments and a screen display image.
-
Etch
In offset lithography an acidified gum solution used to desensitize the non-printing areas of the plate; also, an acid solution added to the fountain water to help keep non-printing areas of the plate free from ink.
-
Expanded Type
A type whose width is greater than normal.
-
Exposure
In photography and platemaking, the step in photographic or photomechanical processes during which light or other radiant energy produces the image on the photo-sensitive coating.
-
F Stops
In photography fixed stops for setting lens apertures. galley proof A proof of text copy before being made into pages. gamma A measure of contrast in photographic images.
-
Fadeometer
An instrument used to measure the fading properties of inks and other pigmented coatings.
-
Fake Color
In color reproduction, producing a color illustration by using one image as a key and making the other separations from it manually.
-
Fanout
In printing, distortion of paper on the press due to waviness in the paper caused by absorption of moisture at the edges of the paper, particularly across the grain.
-
Feeder
In printing presses, the section that separates the sheets and feeds them in position for printing.
-
Felt Side
The smoother side of the paper for printing. The top side of the sheet in paper manufacturing.
-
File
A group of related information, such as text, graphics, page instructions and picture information stored on magnetic disks.
-
Filling In (or filling up)
In letterpress or offset lithography a condition where ink fills the area between the halftone dots or plugs up (fills in) the type.
-
Fixing
Chemical action following development to convert unexposed silver halide to a water-soluble salt and make the image stable and insensitive to further exposure.
-
Flash Exposure
In halftone photography the supplementary exposure given to strengthen the dots in the shadow areas of negatives.
-
Flat
In offset lithography the assembly of negatives on goldenrod paper or positives on film, ready for platemaking. In photography a photograph lacking in contrast.
-
Flatbed Scanner
A device that scans images in a manner similar to a photocopy machine; the original art is positioned face down on a glass plate.
-
Flush Cover
A cover that has been trimmed to the same size as the inside text pages as in this book.
-
Flush Left (or Right)
In composition, type set to line up at the left (or right). This page is set flush left and right.
-
Flush Paragraph
A paragraph with no indention.
-
Flying Paster or Splicer
In web printing, an automatic pasting device that splices a new roll of paper onto an expiring roll, without stopping the press.
-
FM (Frequency Modulation) Screening
A means of digital screening. See stochastic screening.
-
Focal Length
In photography the distance from the center of the lens to the image of an object at infinity. At same size, the distance from copy to image is four times the focal length of the lens.
-
Fog
In photography silver density in the non-image areas.
-
Folio
The page number.
-
Font
In composition, a complete assortment of letters, numbers, punctuations, etc., of a given size and design.
-
Form
In offset, the assembly of pages and other images for printing. In letterpress, type and other matter locked in a chase for printing.
-
Form Rollers
The rollers, either inking or dampening, which directly contact the plate on a printing press.
-
Format
The size, style, type page, margins, printing requirements, etc., of a printed piece.
-
Fountain Solution
In lithography a solution of water, a natural or synthetic gum and other chemicals used to dampen the plate and keep non-printing areas from accepting ink.
-
FPO (For Position Only)
In digital imaging, typically a low-resolution image positioned in a document to be replaced later with a higher resolution version of the same image.
-
Free Sheet
Paper free of mechanical wood pulp.
-
Front End System
In electronic publishing, the workstation or group of workstations containing the applications software for preparing pages of type and graphics.
-
Gapless
Plate or blanket cylinders without gaps.
-
Gathering
In binding, the assembling of folded signatures in proper sequence.
-
GCR (Gray Component Replacement) GCR (Gray Component Replacement) Gear Streaks
In printing, parallel streaks appearing across the printed sheet at the same interval as gear teeth on the cylinder.
-
Generation
Each succeeding stage in reproduction from the original copy.
-
Gigabyte (GB)
One billion bytes.
-
Goldenrod Paper
In offset lithography a specially-coated masking paper of yellow or orange color used by strippers to assemble and position negatives for exposure on plates.
-
Grain
In papermaking, the direction in which most fibers lie which corresponds with the direction in which the paper is made on a paper machine.
-
Grammage
A term in the metric system for expressing the basis weight of paper. It is the weight in grams of a square meter of the paper expressed in g/m2.
-
Gray Balance
The dot values or densities of cyan, magenta and yellow that produce a neutral gray.
-
Gray Level
The number of gray values that can be distinguished by a color separation filter — usually 28 or 256.
-
Gray Scale
A strip of standard gray tones, ranging from white to black, placed at the side of original copy during photography to measure tonal range and contrast (gamma) obtained.
-
Gripper Edge
The leading edge of paper as it passes through a printing press. Also, the front edge of a lithographic or wraparound plate secured to the front clamp of a plate cylinder.
-
Gripper Margin
Unprintable blank edge of paper on which grippers bear, usually 1/2” or less.
-
Grippers
In sheet fed printing presses, metal fingers that clamp on paper and control its flow as it passes through.
-
Groundwood Pulp
A mechanically-prepared wood pulp used in the manufacture of newsprint and publication papers.
-
GUI (Graphical User Interface)
Pronounced “gooey,” in digital imaging, a technical term for a system that lets users manipulate files by pointing to pictures (icons) with a mouse or other pointing device instead of having to type in key commands.
-
Gum Arabic
In offset lithography used in platemaking and on press to protect the non-printing areas of plates.
-
Gumming
In platemaking, the process of applying a thin coating of gum to the non-printing areas of a lithographic plate.
-
Gutter
The blank space or inner margin from printing area to binding.
-
Hairline Register
Register within ±1/2 row of dots.
-
Halation
In photography a blurred effect, resembling a halo, usually occurring in highlight areas or around bright objects.
-
Halftone
The reproduction of continuous-tone images, through a screening process, which converts the image into dots of various sizes and equal spacing between centers (AM screening), or dots of equal size with variable spacing between them (FM screening).
-
Hard Copy
The permanent visual record of the output of a computer or printer on a substrate.
-
Hard Dot
Halftone dot with little or no fringe and prints with little or no dot gain or sharpening. See soft dot.
-
Hard Proof
A proof on paper or other substrate as distinguished from a soft proof which is an image on a VDT screen.
-
Hardware
Computer and peripherals as distinguished from software which is a program for operating hardware.
-
Head Margin
The white space above first line on a page. He/Ne Helium-Neon red laser with wave length of 632 nm.
-
Hickeys
In offset lithography spots or imperfections in the printing due to dirt on the press, dried ink skin, paper particles, etc.
-
High Contrast
n photography a reproduction with high gamma in which the difference in darkness (density) between neighboring areas is greater than in the original.
-
Highlight
The lightest or whitest parts in a photograph represented in a halftone reproduction by the smallest dots or the absence of dots.
-
Holdout
In printing, a property of coated paper with low ink absorption which allows ink to set on the surface with high gloss. Papers with too much holdout cause problems with set-off.
-
HSV
Acronym for hue, saturation and value (or brilliance or luminance) — a color space used in some graphic programs.
-
HTML (HyperText Markup Language)
In imaging for the World Wide Web, the coding language that is used to create Hypertext documents for use on the World Wide Web.
-
Hue
In color, the main attribute of a color which distinguishes it from other colors.
-
Hydrophilic
Water receptive; non-image areas, for example, on an offset plate.
-
Hydrophobic
Water repellent; image areas, for example, on an offset plate.
-
Hypertext
Links to other documents. Words or phrases in the document that are so defined that they can be selected and then cause another document to be retrieved, opened and displayed.
-
ICC (International Color Consortium)
The ICC was established in 1993 for the purpose of creating and promoting the standardization of an open, vendor-neutral, cross-platform system for managing color. ICC specifications for color management can be found at: www.color.org
-
Image Setter
In digital imaging, a generic term that applies to film-output devices for type and graphics. The difference between an imagesetter and a typesetter is in the format of the data that has been converted from discrete-character raster lines to raster data using bitmaps.
-
Imposetter
In digital imaging, an imagesetter capable of outputting a film flat with 4, 8 or more pages in imposed position.
-
Imposition
In image assembly the positioning of pages on a signature so that after printing, folding and cutting, all pages will appear in the proper sequence.
-
Impression Cylinder
In printing, the cylinder on a printing press against which the paper picks up the impression from the inked plate in direct printing, or the blanket in offset printing.
-
Ink Fountain
In printing presses, the device which stores and supplies ink to the inking rollers.
-
Ink Mist
Flying filaments or threads formed by long low-tack inks like newspaper ink. See long Mk.
-
Ink-Jet Printing
In digital printing, a plateless printing system that produces images directly on paper from digital data using streams of very fine drops of dyes which are controlled by digital signals to produce images on paper.
-
Inkometer
In ink testing, an instrument for measuring the tack of printing inks.
-
Insert
A printed piece prepared for insertion into a publication or another printed piece.
-
IR
Abbreviation for infrared radiation above 700 nm.
-
Italic
The style of letters that slant, in distinction from upright, or roman, letters. Used for emphasis within the text.
-
JDF (Job Definition Format)
A data exchange standard that will act as a universal electronic job ticket that contains control data from print buying through estimating, customer service, prepress, press, finishing and dispatch. JDF contains production information rather than content data. See 0IP4.
-
Jog
To align sheets of paper into a compact pile.
-
JPEG (The Joint Photographic Experts Group)
Was formed to create a standard for color and gray scale image compression. JPEG describes a variety of algorithms (rules), each of which is targeted for a type of image application. JPEG is the default format for most digital cameras.
-
Justify
In composition, to space out lines uniformly to line up left and right.
-
Kerning
In typesetting, subtracting space between two characters, making them closer together.
-
Key
To code copy to a dummy by means of symbols, usually letters. Insertions are sometimes keyed in like manner.
-
Keyboard
The input device to input information directly into a typesetter, computer, workstation or, as a stand-alone unit, to record it on paper or magnetic tape.
-
Keyline
In artwork, an outline drawing of finished art to indicate the exact shape, position and size for such elements as half-tones, line sketches, etc.
-
Kilobyte (K or kb or KB)
1024 bytes, the most common measure of computer file length.
-
Kiss Impression
In printing, a very light impression, just enough to produce an image on the paper.
-
Kraft
A paper or board containing unbleached wood pulp (brown in color) made by the sulfate process.
-
Lacquer
A clear resin/solvent coating, usually glossy, applied to a printed sheet for protection or appearance.
-
Laid Paper
Paper with a pattern of parallel lines at equal distances, giving a ribbed effect.
-
Lamination
A plastic film bonded by heat and pressure to a printed sheet for protection or appearance.
-
LAN (Local Area Network)
Communication link in a localized area, such as an office, building, complex of buildings or campus, with technology that provides a high-bandwidth, low-cost medium to which many computer nodes can be connected.
-
Laser (Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation)
The laser is an intense light beam with very narrow bandwidth used in digital-imaging devices to produce images by electronic impulses from computers or facsimile transmission.
-
Layout
The drawing or sketch of a proposed printed piece. In platemaking, a sheet indicating the settings for a step-and-repeat machine.
-
Leaders
In composition, rows of dashes or dots to guide the eye across the page. Used in tabular work, programs, tables of contents, etc.
-
Leading (pronounced ledding)
In composition, the distance between lines of type measured in points.
-
LED
Acronym for light emitting diodes that are used in place of lasers for some output systems.
-
Ledger Paper
A grade of business paper generally used for keeping records where it is subjected to appreciable wear so it requires a high degree of durability and permanence.
-
Letterspacing
The placing of additional space between each letter of a word.
-
Line Copy
Any copy suitable for reproduction without using a halftone screen.
-
Logotype (or logo)
The name of a company or product in a special design used as a trademark in advertising.
-
Long Ink
An ink that has good flow on ink rollers of a press. If the ink is too long, it breaks up into filaments on the press, and causes flying as on a newspaper press.
-
Lowercase
The small letters in type, as distinguished from the capital letters.
-
LPI
Acronym for lines per inch.
-
M
Abbreviation for Mega, which is commonly used to mean one million. In computer terminology, however, M refers to the number 1,048,576, and is used to specify the amount of storage available on a disk or in memory. See megabyte. Also, abbreviation for quantity of 1,000.
-
Machine Coated
Paper which is coated one- or two-sides on a paper machine.
-
Machine Direction
Same as grain direction in paper.
-
Magenta
Hue of a subtractive primary and a four-color process ink. It reflects or transmits blue and red light and absorbs green light.
-
Magenta Screen
A dyed contact screen, used for making halftones.
-
Magnetic Storage
Any disc, film, tape, drum or core that is used to store digital information.
-
Makeover
In platemaking, a plate which is remade.
-
Makeready
In printing, all work done to set up a press for printing.
-
Mask
In color separation photography an intermediate photo-graphic negative or positive used in color correction. In offset lithography opaque material used to protect open or selected areas of a printing plate during exposure.
-
Master
A plate for a duplicating machine. See paper master matte finish Dull paper finish without gloss or lustre.
-
Measure
In composition, the width of type, usually expressed in picas.
-
Mechanical
A term for a camera-ready pasteup of artwork. It includes type, photos, line art, etc., all on one piece of artboard.
-
Mechanical Pulp
In papermaking, groundwood pulp produced by mechanically grinding logs or wood chips. It is used mainly for newsprint and as an ingredient of base stock for lower grade publication papers.
-
Megabyte (Mbyte, MB, Meg, or M)
One million character codes on the computer. One million bytes or characters, often written MB or Mbyte. A unit of measurement equal to 1,024 kilobytes, or 1,048,576 bytes.
-
Megahertz (MHz)
Frequency equal to one million cycles per second. Measures bandwidth or analog electronic signals.
-
Menu
In electronic publishing, a method for selecting alternative functions displayed as a list on a workstation screen. Selection via mouse, key or sequence of keys.
-
Metric System
A decimal system adopted by most countries for solid, liquid and distance measurements. See grammage.
-
Middletones
The tonal range between highlights and shadows of a photograph or reproduction.
-
Modem (MOdulator, DEModulator)
A device that enables a computer to talk to other computers through phone systems by converting computer signals (data) into high-frequency voice communications signals, and vice versa.
-
Moire
In color process printing, the undesirable screen pattern caused by incorrect screen angles of overprinting halftones.
-
Molleton
In offset lithography a thick cotton fabric similar to flannel used on the dampening rollers of a press.
-
Monitor
A video screen on a workstation.
-
Montage
In artwork, several photographs combined to form a composite illustration
-
Mottle
The spotty or uneven appearance of printing, mostly in solid areas.
-
Mouse
In computers, a hand-held device that moves the cursor on a workstation by moving the device on a flat surface.
-
Mullen Tester
A machine for testing the bursting strength of paper.
-
Mylar®
In offset preparation, a polyester film specially suited for stripping positives because of its mechanical strength and dimensional stability.
-
Nanometer
A unit in which wavelengths of light and other radiant energy are expressed. One nanometer is one-billionth of a meter.
-
Negative
In photography film containing an image in which the values of the original are reversed so that the dark areas in the subject appear light on the film and vice versa. See positive.
-
Network
Two or more computers which are linked and share resources to perform related tasks. Group of computers that are connected to each other by communications lines to share information and resources.
-
Newsprint
Paper made mostly from groundwood pulp and small amounts of chemical pulp; used for printing newspapers.
-
Non-Impact Printer
An electronic device like a copier, laser or ink-jet printer that creates images on a surface without contacting it. no-screen exposure See bump exposure.
-
Object-Oriented
In computers, an approach in drawing and layout programs that treats graphics as line and arc segments rather than individual dots. Also called vector-oriented.
-
Oblong
A booklet or catalog bound on the shorter dimension.
-
OCR (Optical Character Recognition)
An electronic means of scanning (reading) copy, and converting the scanned image to an electronic equivalent. The ability to “read” printed text (characters) and convert it to digitized files that can be saved on disk and edited as a text file.
-
Off Loading
Relieving the intensive amount of data processing associated with a specific application (i.e., graphics) from the CPU, by performing those calculations in a dedicated or specialized processor.
-
Off-Press Proofs
Proofs made by photomechanical or digital means in less time and at lower cost than press proofs.
-
Offset
See set-oft In printing, the process of using an intermediate blanket cylinder to transfer an image from the image carrier to the substrate. Short for offset lithography.
-
Offset Gravure
Printing gravure by the offset principle. Generally done on a flexographic press by converting the anilox roller to a gravure image cylinder and covering the plate cylinder with a solid rubber plate.
-
Oleophilic
Oil receptive. See hydrophobic/hydrophilic.
-
Oleophobic Oil Repellent
See hydrophobic/hydrophilic.
-
Opacity
That property of paper which minimizes the show-through of printing from the back side or the next sheet.
-
Opaque
In photoengraving and offset lithography to paint out areas on a negative not wanted on the plate. In paper, the property which makes it less transparent.
-
Opaque Ink
An ink that conceals all color beneath it.
-
OPI (Open Prepress Interface)
An extension to PostScript that automatically replaces low-resolution placeholder images with high-resolution images.
-
Orthochromatic
Photographic surfaces insensitive to red but sensitive to ultraviolet, blue, green and yellow rays.
-
Overhang Cover
A cover larger in size than the pages it encloses.
-
Overlay
In artwork, a transparent covering over the copy where color break, instructions or corrections are marked. Also, trans-parent or translucent prints which, when placed one on the other, form a composite picture.
-
Overlay Proof
A color proof produced with four dyed or pigmented overlay films.
-
Overprinting
Double printing; printing over an area that already has been printed.
-
Overrun
In printing, copies printed in excess of the specified quantity.
-
Packing
In printing presses, material, usually special paper, used to underlay the image or impression cylinder in letterpress, or the plate or blanket in lithography, to get proper squeeze or pressure for printing.
-
Page Buffering
The ability to spool an entire image to disk and print in a continuous motion.
-
Page Makeup
In stripping, assembly of all elements to make up a page. In digital imaging, the electronic assembly of page elements to compose a complete page with all elements in place on a video display terminal and on film or plate.
-
Pagination
In computerized typesetting, the process of performing page makeup automatically.
-
Palette
In computers, the collection of colors or shades available to a graphic system or program.
-
Panchromatic
Photographic film sensitive to all visible colors.
-
Paper Master
A paper printing plate used on an offset duplicator. The image is made by hand drawing, typewriter or electro photography.
-
Paste Dryer
In inkmaking, a type of dryer, usually a combination of drying compounds.
-
PC
Acronym for personal computer.
-
PDF (Portable Document File)
PDF is a universal electronic file format, modeled after the PostScript language and is device-and resolution-independent. Documents in the PDF format can be viewed, navigated and printed from any computer regardless of the fonts or software programs used to create the original.
-
Perfecting Press
A printing press that prints both sides of the paper in one pass through the press.
-
pH
A number used for expressing the acidity or alkalinity of solutions. A value of 7 is neutral in a scale ranging from 0 to 14. Solutions with values below 7 are acid, above 7 are alkaline.
-
Photoconductor
In digital imaging, materials used in electrophotography which are light sensitive when charged by corona.
-
Photomechanical
In platemaking, pertaining to any platemaking process using photographic negatives or positives exposed onto plates or cylinders covered with photosensitive coatings.
-
Photopolymer Coating
In photomechanics, a plate coating consisting of compounds which polymerize on exposure to produce tough abrasion-resistant plates capable of long runs especially when baked in an oven after processing.
-
Pica
Printer’s unit of measurement used principally in typesetting. One pica equals approximately 1/6 of an inch.
-
Picking
In printing, the lifting of the paper surface during printing. It occurs when pulling force (tack) of ink is greater than surface strength of paper.
-
PICT
In digital imaging, a standard data format with which most Macintosh illustrations are encoded.
-
Pigment
In printing inks, the fine solid particles used to give inks color, transparency or opacity.
-
Piling
In printing, the building up or caking of ink on rollers, plate or blanket; will not transfer readily. Also, the accumulation of paper dust or coating on the blanket of offset press.
-
Pin Register
In copy preparation, the use of accurately positioned holes and special pins on copy, film, plates and presses to insure proper register or fit of colors.
-
Pixel
Short for “picture element.” A pixel is the smallest resolvable point of a raster image. It is the basic unit of digital imaging.
-
Plate Cylinder
The cylinder of a press on which the plate is mounted.
-
Platesetter
An image recorder which images directly on plate material. Platesetters currently available use lasers to expose or image paper, polyester or aluminum plates.
-
PMS (Pantone Matching System)
Color charts that have over 700 preprinted color patches of blended inks, used to identify, display or define special colors.
-
PMT (Photomultiplier Tube)
A light-sensitive sensor that can sense very low light levels by amplifying the signals applied to it during the sensing. PMTs give drum scanners their superior color separation capabilities.
-
Point
Printer’s unit of measurement, used principally for designating type sizes. There are 12 points to a pica; approximately 72 points to an inch.
-
Poor Trapping
In printing, the condition in wet printing in letterpress and lithography when less ink transfers to previously printed ink than to unprinted paper. Also called undertrapping.
-
Porosity
The property of paper that allows the permeation of air, an important factor in ink penetration.
-
Portrait
In photography vertical orientation of a format as opposed to landscape horizontal orientation.
-
Position Proof
Color proof for checking position, layout and/or color breakout of image elements.
-
Positive
In photography film containing an image in which the dark and light values are the same as the original. The reverse of negative.
-
PostScript®
A page description language developed by Adobe Systems, Inc. to describe an image for printing. It handles both text and graphics. A PostScript file is a purely text-based description of a page.
-
Preflighting
In digital prepress, the test used to evaluate or analyze every component needed to produce a printing job. Preflight confirms the type of disk being submitted, the color gamut, color breaks, and any art required (illustrations, transparencies, reflective photos, etc.) plus layout files, screen fonts, printer fonts, EPS or TIFF files, laser proofs, page sizes, print driver, crop-marks, etc.
-
Presensitized Plate
In photomechanics, a metal, film or paper base plate that has been precoated with a light-sensitive coating.
-
Press Proofs
In color reproduction, a proof of a color subject made on a printing press, in advance of the production run.
-
Pressure-Sensitive Paper
Material with an adhesive coating, protected by a backing sheet until used.
-
Print Quality
A term describing the visual impression of a printed piece. In paper, the properties of the paper that affect its appearance and the quality of reproduction.
-
Process Colors
In printing, the subtractive primaries: yellow, magenta and cyan, plus black in four-color process printing.
-
Process Lens
A highly corrected photographic lens with a flat field for graphic arts line, halftone and color photography.
-
Process Printing
The printing from a series of two or more halftone plates to produce intermediate colors and shades.
-
Program
In computers, sequence of instructions for a computer. Same as software
-
Psychrometer
A wet-and-dry bulb type of hygrometer. Considered the most accurate of the instruments practical for industrial plant use for determining relative humidity.
-
Quality Control
A program of activities including customer service, process control and sampling with the objective of eliminating causes of process variability now called Statistical Process Control.
-
Ragged Left
In typesetting, type that is justified on the right margin and ragged on the left.
-
Ragged Right
In typesetting, type that is justified on the left margin and ragged on the right.
-
Raster Image Processor (RIP)
In digital imaging, a combination of computer software and hardware that controls the printing process by calculating the bitmaps of images and instructing a printing device to create the images. Most PostScript systems use a hardware RIP built into the printer.
-
Ream
Five hundred sheets of paper.
-
Reducers
In printing inks, varnishes, solvents, oily or greasy compounds used to reduce the consistency for printing. In photography chemicals used to reduce the density of negative or positive images or the size of halftone dots (dot etching).
-
Reflection Copy
In photography illustrative copy that is viewed and must be photographed by light reflected from its surface. Examples are photographs, drawings, etc.
-
Register
In printing, fitting of two or more printing images in exact alignment with each other.
-
Register Marks
Crosses or other targets applied to original copy prior to photography. Used for positioning films in register, or for register of two or more colors in process printing.
-
Relative Humidity (RH)
The amount of water vapor present in the atmosphere expressed as a percentage of the maximum that could be present at the same temperature.
-
Repeatability
The ability to keep photo film and the images thereon in proper register in imagesetters and film plotters. Repeatability is usually measured in micrometers.
-
Reprography
Copying and duplicating.
-
Resist
In photomechanics, a light-hardened stencil to prevent etching of non-printing areas on plates.
-
Resolution
Ability of an input device to record, or an output device to reproduce the fine detail of an image. There is a difference between resolution and addressability or sampling rate. Resolution concerns how closely spots can be placed, and also whether gray levels can be distinguished. Resolution for output devices depends on addressability, bit-depth, mark size and color.
-
Respi Screen
In halftone photography a contact screen with 110-line screen ruling in the highlights and 220-line in the middle tones and shadows to produce a longer scale and smoother gradation of tones in the light areas of the copy.
-
Retrofit
Backwards integration of advanced capability into a device or program not originally intended for that purpose.
-
Reverse Angle Doctor Blade
In flexography, similar to doctor blade in gravure except used with much lighter pressure and a reverse angle on the anilox roll.
-
RGB (red, green and blue)
The primary additive colors used in display devices and scanners. Commonly used to refer to the color space, mixing system or monitor in color computer graphics.
-
Right-Angle Fold
In binding, a term used for two or more folds that are at 90° angles to each other.
-
RIP
See raster image processor.
-
Roller Stripping
In lithography a term denoting that the ink does not adhere to the metal ink rollers on a press. rub-proof In printing, an ink that has reached maximum dryness and does not mar with normal abrasion.
-
Run-Around
In composition, the term describing type set to fit around a picture or other element of the design.
-
Runnabilit
Paper properties that affect the ability of the paper to run on the press.
-
Running Head
A headline or title repeated at the top of each page.
-
Saddle Stitch
In binding, to fasten a booklet by wiring it through the middle fold of the sheets. Also called saddle wire.
-
Safelight
In photography the special darkroom lamp used for illumination without fogging sensitized materials.
-
Sample
Basic optical image element (analog) taken by the image sensor of a camera or scanner. A sample may be black and white, or it can be for several color channels. The sample is processed to obtain a pixel. Processing may involve conversion from device ROB to some standardized color space.
-
Scaling
Determining the proper size of an image to be reduced or enlarged to fit an area.
-
Scan-A-Web
In web printing, a rotating mirror arrangement where speed can be varied to match the speed of a press so the image on paper can be examined during printing.
-
Scanner
An electronic device used in the making of color and tone-corrected separations of images
-
Score
To impress or indent a mark in the paper to make folding easier.
-
Screen Angles
In color reproduction, angles at which the halftone screens are placed in relation to one another, to avoid undesirable moire patterns. A set of angles often used is: black 450, magenta 75°, yellow 90°, cyan 105°.
-
Screen Ruling
The number of lines or dots per inch on a halftone screen.
-
Screened Print
In photography a print with a halftone screen made from a halftone negative or by diffusion transfer.
-
Screening
That part of a RIP which calculates the tonal values of each spot for an output device on the basis of the required tonal value of the projected pixel from the input, in order to form the screener dots. The function of a screener is device dependent. Depending on the characteristics of the output device, the screener dots can have very different properties.
-
SCSI (Small Computer Systems Interface)
Pronounced “skuzzy,” SCSI is an interface used to transmit digital data and to connect computers to peripherals. An industry-standard interface for hard drives and other storage devices that allows for very fast transfers of information.
-
Scum
In offset lithography, a film of ink printing in the non-image areas of a plate where it should not print.
-
Self Cover
A cover of the same paper as inside text pages.
-
Semi-Chemical Pulp
A combination of chemical and mechanical pulping with properties similar to chemical pulp.
-
Sensitivity Guide
A continuous-tone gray scale with numbered steps used to control exposures in plalemaking and lithfilm photography.
-
Serif
The short cross-lines at the ends of the main strokes of many letters in some typefaces.
-
Server
A file server provides file data interchange between compatible peripheral devices on a local area network. Servers are identified by the type of resource they provide (e.g., disk server, file server, printer server, communications server).
-
Set-Off
In presswork, when the ink of a printed sheet rubs off or marks the next sheet as it is being delivered. Also called offset.
-
SGML (Standard Generalized Mark-up Language)
One of the newer languages for marking text for a variety of purposes, including typesetting and disk publishing. A well-designed SGML scheme enables the publisher to mark text just once for multiple uses.
-
Shadow
The darkest parts in a photograph, represented in a halftone by the largest dots.
-
Sharpen
To decrease in color strength, as when halftone dots become smaller; opposite of dot spread or dot gain.
-
Sheetwise
To print one side of a sheet of paper with one plate, then turn the sheet over and print the other side with another plate using same gripper and opposite side guide.
-
Shingling
In image assembly and layouts, the center or gutter margin is varied according to the position of the page in the sig-nature and the bulk of the paper. See creep.
-
Short Ink
An ink that is buttery and does not flow freely.
-
Show-Through
In printing, the undesirable condition in which the printing on the reverse side of a sheet can be seen through the sheet under normal lighting conditions.
-
Side Guide
On sheetfed presses, a guide on the feed board to position the sheet sideways as it feeds into the front guides before entering the impression cylinder.
-
Signature
In printing and binding, the name given to a printed sheet after it has been folded.
-
Silhouette Halftone
A halftone of a subject with all of the background removed.
-
Sizing
The treatment of paper which gives it resistance to the penetration of liquids (particularly water) or vapors.
-
Skid
A platform support for a pile of cut sheets of paper.
-
Slitting
Cutting printed sheets or webs into two or more sections by means of cutting wheels on a press or folder.
-
Small Caps
An alphabet of SMALL CAPITAL LETTERS available in most roman typefaces approximately the size of the lowercase letters. Used in combination with larger capital letters.
-
Soft Dot
Halftone dot with considerable fringe which causes dot gain or sharpening in printing or photography.
-
Soft Ink
Descriptive of the consistency of paste inks.
-
Soft Proof
See hard proof.
-
Spectrophotometer
Instrument for measuring color for CIE color spaces. It is more accurate than most color colorimeters.
-
Spectrum
The complete range of colors in the rainbow, from short wavelengths (blue) to long wavelengths (red).
-
Spiral Binding
A book bound with wires in spiral form inserted through holes punched along the binding side.
-
Spool (Simultaneous Peripheral Operations OnLine)
Refers to an output data set that is waiting for a print device.
-
Spot
The smallest element of the addressability grid of an output device. Similar to a pixel, a spot is data, not something that can be seen. A spot is what the screener intended to form. A mark is what the marking engine actually placed at a spot location. A spot has a spatial aspect (size and location in the addressability grid), and a tonal and color aspect.
-
Spreads and Chokes
See chokes and spreads.
-
Star Target
Film pinwheel used to measure resolution of plates during production and degradation during printing.
-
Static Neutralizer
In printing presses, an attachment designed to remove the static electricity from the paper to avoid ink set-off and trouble with feeding the paper.
-
Step-and-Repeat
In photomechanics, the procedure of multiple exposure using the same image by stepping it in position according to a predetermined layout or program.
-
Stet
A proofreader’s mark, written in the margin, signifying that copy marked for corrections should remain as it was.
-
Stochastic Screening
A digital screening process that converts images into very small dots (14-40 microns) of equal size and variable spacing. Second order screened images have variable size dots and variable spacing. Also called Frequency Modulated (FM) screening.
-
Stock
Paper or other material to be printed.
-
Stock Photography
Used widely by creative professionals in need of ready-made images that illustrate a specific lifestyle, scene, mood or process. Some stock images are royalty-free, but most carry a fee based on usage.
-
Stone
In lithography formerly used as the plate material and presently used by artists as an art medium. In letterpress, the bed on which metal type is leveled and locked up.
-
Strike-On Composition or Cold Type
Type set on typewriter composing machines.
-
Stripping
In image assembly the positioning of negatives (or positives) on a flat to compose a page or layout for platemaking. In printing, ink stripping on ink rollers prevented by plastic or copper coated steel rollers in the ink roller train.
-
Substance
The weight in pounds of a ream (500 sheets) of paper cut to the standard size (17” x 22”) for business papers (bond and ledger): e.g., 20 pounds. Similar to basis weight of other grades of paper.
-
Substrate
Any material that can be printed on, such as paper, plastic and fabric.
-
Subtractive Primaries
Yellow, magenta and cyan, the hues used for process color printing inks.
-
Sulphate Pulp
Paper pulp made from wood chips cooked under pressure in a solution of caustic soda (sodium hydroxide) and sodium sulphide. Known as kraft.
-
Sulphite Pulp
Paper pulp made from wood chips cooked under pressure in a solution of bisulphite of lime (calcium bisulphite).
-
Supercalender
In papermaking, a calender stack, separate from the papermaking machine, with alternate metal and resilient rolls, used to produce a high finish on paper.
-
Supercell
In digital halftone imaging, a combination of subgroups of halftone dots that are handled as a single group.
-
Surprint
In photomechanics, exposure from a second negative or flat superimposed on an exposed image of a previous negative or flat.
-
Tack
In printing inks, the property of cohesion between particles; the separation force of ink needed for proper transfer and trapping on multicolor presses. A tacky ink has high separation forces and can cause surface picking or splitting of weak papers.
-
Tagged Image File Format (TIFF)
A file format for graphics suited for representing scanned images and other large bitmaps. TIFF is a neutral format designed for compatibility with all applications. TIFF was created specifically for storing gray-scale images, and it is the standard format for scanned images such as photographs — now called TIFF/IT.
-
Terabyte (TB)
One trillion bytes.
-
Text
The body matter of a page or book, as distinguished from the headings.
-
The Internet
A network of networks that links workstations over telecommunication lines to share files and exchange e-mail internationally.
-
Thermal Transfer Printers
These printers use a transfer sheet that carries ink in contact with the paper or transparency, and a heated printhead driven by digital data that touches the transfer sheet to transfer images to the right points on the page.
-
Thermal Dye Sublimation
Like thermal printers, except pigments are vaporized and float to desired proofing stock. Similar to Thermal Dye Diffusion Transfer, or D2T2.
-
Thermo-Mechanical Pulp
In papermaking, made by steaming wood chips prior to and during refining, producing a higher yield and stronger pulp than regular groundwood.
-
Thixotropy
False body in inks.
-
Tints
Various even tone areas (strengths) of a solid color.
-
Tissue Overlay
A thin, translucent paper placed over artwork (mostly mechanicals) for protection; used to indicate color break and corrections.
-
Tolerances
The specification of acceptable variations in register, density, dot size, plate or paper thickness, concentration of chemicals and other printing parameters.
-
Tone Reproduction
The tonal relationship between all the elements of a reproduction.
-
Toner
In digital printing, imaging material also called digital inks, used in plateless printing systems like electrophotography, magnetograph, ion or electron deposition and laser printers . In inks, dye used to tone printing inks, especially black.
-
Tooth
A characteristic of paper, a slightly rough finish, which permits it to take ink readily.
-
Transparency
Color positive film.
-
Transparent Copy
In photography illustrative copy such as a color transparency or positive film through which light must pass in order for it to be seen or reproduced.
-
Transpose
To exchange the position of a letter, word or line with another letter, word or line,
-
Trapping
In printing, the ability to print a wet ink film over previously printed ink. Dry trapping is printing wet ink over dry ink. Wet trapping is printing wet ink over previously printed wet ink. In prepress, refers to how much overprinting colors overlap to eliminate white lines between colors in printing. See spreads and chokes.
-
Trim Marks
In printing, marks placed on the copy to indicate the edge of the page.
-
Twin-Wire Machine
In papermaking, a fourdrinier paper machine with two wires instead of one producing paper with less two-sidedness.
-
Two-Sheet Detector
In printing presses, a device for stopping or tripping the press when more than one sheet attempts to feed into the grippers.
-
Two-Sidedness
In paper, the property denoting difference in appearance and printability between its top (felt) and bottom (wire) sides.
-
Type Gauge
In composition, a printer’s tool calibrated in picas and points used for type measurement.
-
UCA (UnderColor Addition)
In process color printing, used with GOR, UCA is ink added in shadow areas to increase color saturation.
-
UCR (UnderColor Removal)
In process multicolor printing, color separation films are reduced in color in, neutral areas where all three colors overprint and the black film is increased an equivalent amount in these areas. This improves trapping and can reduce makeready and ink costs.
-
UGRA Test Target
A measure of image resolution and dot size on plates and in printing.
-
Undercut
In printing presses, the difference between the radius of the cylinder bearers and the cylinder body, to allow for plate (or blanket) and packing thickness.
-
Unit
In multicolor presses, refers to the combination of inking, plate and impression operations to print each color. A 4-color press has four printing units each with its own inking, plate and impression functions.
-
UNIX
A multiuser, multi-tasking operating system that runs on a wide variety of computer systems from micro to mainframe, UNIX was written in the C programming language. It is the most common operating system for servers on the Internet.
-
Up
In printing, two-up, three-up, etc., refers to imposition of material to be printed on a larger size sheet to take advantage of full press capacity.
-
Uppercase
Capital letters in type.
-
UV Inks
In printing, solventless inks that are cured by UV radiation. They are used extensively in screen printing, narrow web letterpress and flexographic printing. vacuum frame In platemaking, a vacuum device for holding copy and reproduction material in contact during exposure.
-
Varnish
A thin, protective coating applied to a printed sheet for protection or appearance. Also, in inkmaking, it can be all or part of the ink vehicle.
-
Vehicle
In printing inks, the fluid component which acts as a carrier for the pigment.
-
Vellum Finish
In papermaking, a toothy finish which is relatively absorbent for fast ink penetration.
-
Video Display Terminal (VDT)
A term for a computer monitor or display.
-
Vignette
An illustration in which the background fades gradually away until it blends into the unprinted paper.
-
Viscosity
In printing inks, a broad term encompassing the properties of tack and flow.
-
WAN (Wide Area Network)
Any Internet or network that covers an area larger than a single building or campus. A collection of disparate, widely located and geographically isolated networks, connected by private or public communication lines.
-
Warm Color
In printing, a color with a yellowish or reddish cast.
-
Washup
The process of cleaning the rollers, form or plate, and sometimes the ink fountain of a printing press.
-
Waterless Plate
In platemaking, printing plate with silicone rubber coating in non-image areas, that is printed on an offset press without dampening solution.
-
Waterless Printing
In offset, printing on a press using special waterless plates and no dampening system.
-
Web
A roll of paper used in web or rotary printing.
-
Web Press
A press which prints on a roll of paper.
-
Web Tension
The amount of pull or tension applied in the direction of travel of a web of paper by the action of a web press.
-
Widow
In composition, a single word or part of a word on a line by itself, ending a paragraph, or starting a page, frowned upon in good typography.
-
Wire Side
In papermaking, the side of a sheet next to the wire in manufacturing; opposite from felt or top side.
-
Wire-O Binding
A continuous double series of wire loops run through punched slots along the binding side of a booklet.
-
With The Grain
Folding or feeding paper into a press with the grain of the paper parallel to the blade of the folder or the axis of the impression cylinder.
-
Woodcut
An illustration in lines of varying thickness, cut in relief on plank-grain wood, for the purpose of making prints by a relief printing method like letterpress.
-
Word Processor
A typewriter connected to a computerized recording medium to input, edit and output digital text data.
-
Work-And-Tumble
To print one side of a sheet of paper, then turn it over from gripper to back using the same side guide and plate to print the second side.
-
Work-And-Turn
To print one side of a sheet of paper, then turn it over from left to right and print the second side using the same gripper and plate but opposite side guide.
-
WORM (Write Once Read Many Times)
A type of optical memory device.
-
Wove Paper
Paper having a uniform unlined surface and a soft smooth finish.
-
Wraparound Plate
In rotary letterpress, a thin one-piece relief plate which is wrapped around the press cylinder like an offset plate. Can be used for direct or indirect (offset) printing.
-
Wrinkles
Creases in paper occurring during printing. In inks, the uneven surface formed during drying.
-
Wrong Font
In proofreading, the mark “WF” indicates a letter or figure of the wrong size or typeface.
-
WWW (World Wide Web)
The highly inter-connected network of hypertext servers (HTTP servers) which allow text, graphics, sound and video files to be displayed.
-
WYSIWYG (What You See Is What You Get)
Means that what you see on the computer monitor is generally the same as what appears on the hard copy or film. Pronounced “wizzywig.”
-
Xerography
An electrophotographic copying process that uses a corona charged photoconductor surface, electrostatic forces and dry or liquid toner to form an image.
-
XML (eXtensible Mark-up Language)
A more powerful mark-up language than the previously popular HTML. XML allows designers and programmers to create tags that can do almost anything they want, hence the term “extensible.” XML was created so that richly structured documents could be used over the Web.
-
Yellow
Hue of a subtractive primary and a four-color process ink. It reflects red and green light and absorbs blue light.